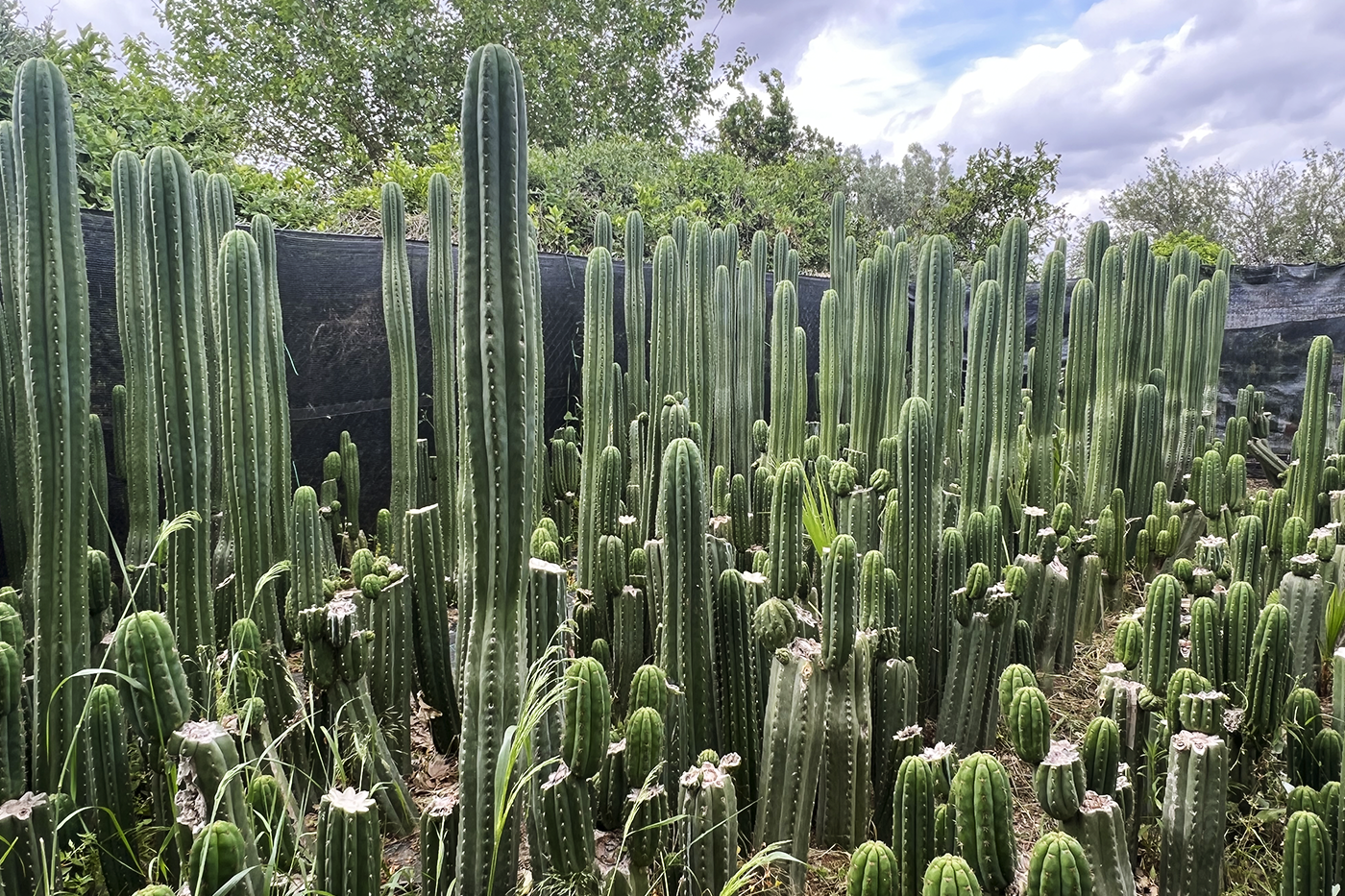
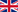
Trichocereus, a genus of cacti native to South America, has attracted interest not only for its ornamental beauty and medicinal properties, but also for its potential to contribute to climate change mitigation. In this article, we explore how this cactus can play a role in addressing the climate crisis—focusing on its ability to act as a carbon sink, its traditional uses, and its potential in sustainable cultivation.
What Is Trichocereus?
The Trichocereus genus includes several species of columnar cacti, with Trichocereus macrogonus var. pachanoi—commonly known as the San Pedro cactus—being one of the most notable. Native to the Andean regions of Ecuador, Peru, and Bolivia, this cactus has been used for thousands of years in cultural and medicinal contexts.
Trichocereus as a Carbon Sink
One of the most important ecological roles of Trichocereus in mitigating climate change is its ability to store carbon.
🌿 Carbon Storage Through Photosynthesis
Like all plants, Trichocereus absorbs carbon dioxide (CO₂) through photosynthesis and releases oxygen. What makes it particularly effective is its drought tolerance, allowing it to store carbon in its tissues over long periods, even in harsh environments.
✅ Long-Term Carbon Retention
Cacti such as Trichocereus have a unique structure that enables them to retain large amounts of carbon, helping to reduce atmospheric CO₂ levels. This makes them valuable allies in the fight against global warming.
✅ Sustainable Cultivation
Growing Trichocereus using sustainable practices supports both reforestation and land restoration efforts. Due to its low water requirements, it’s an ideal species for sustainable agriculture in arid and semi-arid zones.
Traditional Uses and Cultural Impact
The traditional use of Trichocereus in indigenous Andean cultures underscores its spiritual and cultural significance—which adds another dimension to its ecological value.
🌎 Culture and Spirituality
San Pedro cactus has long been used as a sacred plant, believed to facilitate connection with the divine and induce altered states of consciousness. In times of environmental crisis, reviving these cultural practices can promote a deeper environmental ethics rooted in respect for nature.
🌱 Environmental Education and Awareness
The cultural significance of Trichocereus can serve as a powerful educational tool. By integrating traditional ecological knowledge into modern sustainability education, we can increase the effectiveness of climate change mitigation strategies at the community level.
Challenges of Cultivation Under a Changing Climate
Despite its resilience, Trichocereus is not immune to the challenges posed by climate variability. Shifts in rainfall patterns and temperature extremes can impact its growth and survival.
It is therefore essential to develop adaptive cultivation techniques to ensure that Trichocereus remains a viable species under future climate scenarios. This includes:
-
Selecting climate-resilient varieties
-
Using water-saving irrigation methods
-
Monitoring soil pH and microclimates
🌍 Conclusion
Trichocereus is more than just a cactus—it represents a unique fusion of ecological value and cultural heritage. Its potential for carbon storage, spiritual relevance, and suitability for sustainable farming makes it a powerful ally in the global effort to combat climate change.
Promoting further research and implementation of sustainable cultivation practices can help integrate Trichocereus into larger climate resilience strategies. When used responsibly, this remarkable plant can contribute to both ecological conservation and the preservation of ancestral traditions.
In short, Trichocereus sits at a fascinating intersection between nature and culture, and if nurtured sustainably, it can play a key role in mitigating climate change for generations to come.