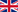
Grafting is a key technique for expert cactus growers looking to enhance resilience, accelerate growth, and propagate unique Trichocereus varieties. The Trichocereus is an ideal rootstock due to its fast growth and durability, making it perfect for supporting more delicate species.
This guide covers advanced grafting techniques to ensure optimal success in this process.
Why Graft on Trichocereus?
The Trichocereus Pachanoi and similar species are highly valued as grafting rootstocks for several reasons:
- Fast growth: These cacti grow quickly and help the grafted plant thrive.
- Disease resistance: Trichocereus rootstocks are more resistant to diseases, providing strong support for grafts.
- Climate adaptability: These cacti can withstand a range of environmental conditions, making them a versatile choice for grafting in both dry and humid climates.
Essential Tools and Preparation for Grafting
Before starting, ensure you have the right tools and that both the rootstock and the scion (the plant to be grafted) are prepared:
- Sterilized knife: A sharp, sterilized knife is critical for making clean cuts that maximize graft success.
- Elastic bands or grafting tape: These are used to secure the graft until the plants fuse.
- Rooting hormone (optional): This can speed up the healing process and improve graft success.
Advanced Grafting Techniques for Trichocereus
Grafting Trichocereus is relatively straightforward, but advanced growers often use techniques that ensure a more efficient and effective union between the scion and the rootstock. Below are some of the most effective methods:
1. Flat or Slant Grafting
This is the most common and effective technique, especially for small and delicate species. Here’s the process:
- Step 1: Make a clean horizontal cut on the top of the Trichocereus, ensuring the surface is flat.
- Step 2: Make a similar cut on the base of the scion.
- Step 3: Place the scion on the rootstock, aligning the vascular rings (the areas where the sap circulates). This alignment is essential for nutrient transfer.
- Step 4: Use an elastic band to secure the graft firmly but gently. Keep the plant in a bright area without direct sunlight until the graft heals.
2. Inclined Grafting
This method works particularly well for grafting smaller cacti or species that naturally lean to one side.
- Step 1: Instead of a flat cut, make an angled cut on both the rootstock and scion.
- Step 2: Join the two pieces so that the cut surfaces align perfectly. This creates a larger surface area for contact, improving the union.
- Step 3: Secure the graft with grafting tape, ensuring the parts don’t shift during the healing process.
3. Multiple Grafts on One Rootstock
For expert growers looking to produce a plant with multiple grafts on one Trichocereus, this technique allows you to propagate several species on a single cactus.
- Step 1: Make several clean cuts around the top of the Trichocereus, leaving enough space between each.
- Step 2: Prepare multiple small scions and place them on each cut area, ensuring the vascular rings align.
- Step 3: Secure each graft individually using small strips of tape or elastic bands. Be sure to monitor the grafts closely during the healing process.
Key Factors for Grafting Success
- Alignment of Vascular Rings: Correct alignment between the rootstock and scion is essential for a successful graft. If the rings do not match, the scion will not receive nutrients and will not survive.
- Light and Temperature Conditions: After grafting, keep the plant in a warm, bright location with indirect sunlight to prevent the scion from drying out.
- Controlled Humidity: Avoid high humidity during the healing process, as it can promote fungal growth and compromise the graft.
Post-Grafting Care
Once the graft has healed, typically within 2-4 weeks, you can gradually expose the plant to direct sunlight and resume regular watering. Regularly check the graft to ensure there are no signs of rejection, such as browning or shrinking. With proper care, the grafted plant will grow vigorously and could even flower earlier than if it had remained on its original rootstock.
Conclusion
Grafting in Trichocereus is an advanced technique that allows growers to achieve incredible results, from propagating rare species to creating stunning ornamental plants. With patience, precision, and the right techniques, you can master the art of grafting and enjoy the benefits of stronger, faster-growing cacti.